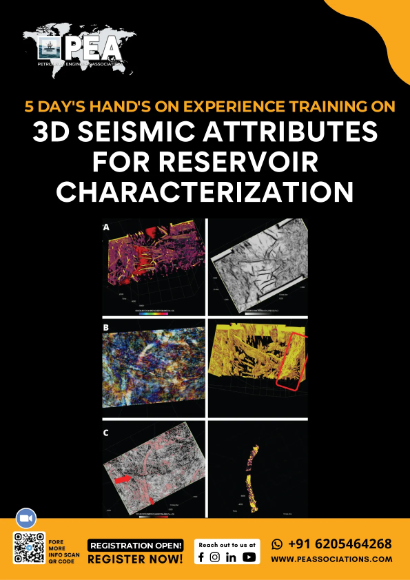
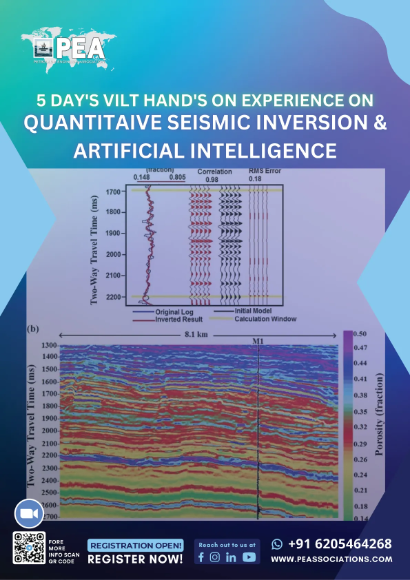
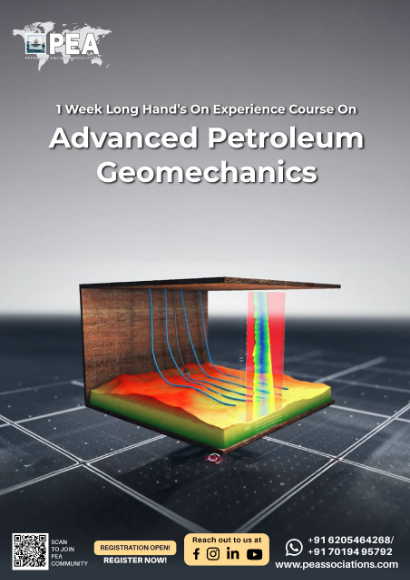
Applied Machine Learning for Geology and Geophysics
Have Questions ?
Applied Machine Learning for Geology and Geophysics - ML-GG6
| Code | Date | Time | Duration | Location | Currency | Team of 10 Per Person | Team of 7 Per Person | Early Bird Fee Per Person | Normal Fee Per Person |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML-GG6 | 06 - 17 Jul 2026 | 9:30 PM Indian Time |
4 Hours Per Day
|
Zoom Online
|
USD
|
1500
|
1850
|
2000
|
2500
|
The classes will be conducted online via Zoom from Monday to Friday for 2 weeks, for 4 hours per day excluding breaks.
Boost your team's skills and your budget! Enjoy group discounts for collaborative learning. Send an inquiry to info@peassociations.com.
Applied Machine Learning for Geology and Geophysics
This course provides participants with a comprehensive understanding of how machine learning (ML) techniques can be applied to solve geological and geophysical problems. It focuses on integrating ML workflows with traditional subsurface interpretation to improve prediction accuracy, automate data analysis, and enhance reservoir understanding.
Description
The Applied Machine Learning for Geology and Geophysics course bridges the gap between geoscience and data science by demonstrating how modern machine learning methods can be used to analyze, interpret, and predict subsurface properties.
Participants will learn key ML concepts — including supervised and unsupervised learning, data preprocessing, feature selection, and model evaluation — and how to apply them to geological and geophysical datasets such as well logs, seismic attributes, and core data.
Through hands-on examples and case studies, the course highlights applications such as lithofacies classification, seismic inversion, porosity and permeability prediction, fault and fracture detection, and reservoir property mapping.
The focus is on practical implementation — helping geoscientists use ML tools and techniques to support exploration, development, and production decision-making.
As the oil and gas industry increasingly adopts digital technologies, machine learning has become a powerful tool for extracting insights from large and complex geoscience datasets.
This course introduces participants to the fundamentals of ML algorithms and demonstrates their application in geology and geophysics. Participants will gain the skills to build predictive models, integrate data-driven insights with geological understanding, and enhance reservoir characterization and risk assessment.
Understand key concepts and workflows of machine learning.
Prepare, clean, and process geoscience datasets for ML applications.
Apply supervised and unsupervised learning methods to geological and geophysical problems.
Perform lithofacies, clustering, and regression analysis using well and seismic data.
Integrate ML outputs with geological interpretation and reservoir modeling.
Evaluate model performance and uncertainty for reliable predictions.
Recognize limitations and best practices in ML for subsurface studies.
The course combines lectures with practical demonstrations, coding exercises (in Python or similar platforms), and case studies from real exploration and development projects. Participants will work through ML workflows — from data preprocessing to model deployment — using industry-relevant examples to build confidence and capability in applying ML techniques.
Improved data analysis and predictive modeling for exploration and development.
Enhanced reservoir characterization and reduced interpretation uncertainty.
Increased efficiency through automation of repetitive interpretation tasks.
Strengthened integration of geoscience and digital technologies.
Capability development for data-driven decision-making within technical teams.
Gain practical experience in applying ML techniques to geoscience data.
Learn to interpret and validate model outputs in geological context.
Strengthen analytical and programming skills for digital workflows.
Develop a strong understanding of how ML supports geoscience innovation.
Enhance technical and professional value in modern subsurface analysis.
Geologists and Geophysicists
Petrophysicists and Reservoir Engineers
Data Scientists working in the energy sector
Subsurface Analysts and Geomodellers
Introduction to Python
Introduction to numpy
Introduction to pandas
Introduction to Seaborn
Pandas built in data visualization
Manipulating las files
lasio library
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) on las data
Univariate EDA
Understanding Standardization vs Normalization (linear)
Application of Quantile transform (non linear)
Understanding a Q-Q plot
Generating QQ plots for all curves
Unsupervised Learning: Clustering
KMeans: SELF ORGAINIZING MAPS (SOM)
Feature importance, selection and extraction
Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE)
Recursive Feature Elimination with Cross Validation (RFECV)
Other approaches worth considering
Supervised Learning: Regression
Feature importance, selection and extraction
KFold Cross Validation
Repeated KFold Cross Validation
Regression metrics in scikitlearn
Understanding ensemble models
Support Vector Machines: Regression (SVR)
Multi Layer Perceptron (MLP): Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
UnSupervised Machine Learning: Seismic Data
Read in horizon data
Gridding horizon data
Reading spatial coordinates of traces from segy header
Cropping seismic segy
Viewing seismic in Opendtect
Extracting attributes
Trace sampling of all attribute segy volume
Exploratory Data Analysis on csv file
Generate a list of all segys in directory
Read in the previously sampled traces
Apply Principle Component Analysis (PCA) to reduce features
Analyze contribution of each principle component using biplot
Understand PCA loadings
Apply PCA before clustering
KMeans: determine optimum number of clusters
Feature (seismic attribute) importance, selection, and extraction
t-SNE (t distribution Stochastic Neighborhood Embedding)
DBSCAN (Density Based Spatial Clustering Appplication with Noise)
Building Self Organizing Maps (SOM) unsupervised clustering models
Generating segy of clusters and viewing results in Opendtect
Using geobody filtering to enhance stratigraphic features
Testing several node topologies and viewing/analyzing results in Opendtect
On successful completion of this training course, PEA Certificate will be awarded to the delegates.
Sami Elkurdy serves as the expert trainer for the Applied Machine Learning for Geology and Geophysics course. He is a geophysicist with over 45 years of experience in the oil industry, having worked with exploration and development companies worldwide. This background provides extensive international exposure across diverse geological basins with varied structural and stratigraphic settings.
Elkurdy possesses deep expertise in seismic interpretation and processing, which he has extended into machine learning applications. His skills effectively bridge geophysics and ML, enabling practical integration of these disciplines. He now operates as an Independent Consultant, delivering technical services in geophysics and machine learning alongside specialized training courses
Frequently Asked Questions
All course bookings made through PEA are strictly non-refundable. By registering for a course, you acknowledge and accept that all fees are payable in full and are not subject to refund under any circumstances, including changes in personal or professional commitments or partial attendance.
PEA reserves the right to make reasonable adjustments to course content, trainers, or schedules where necessary, without entitling delegates to a refund. Comprehensive details of each course — including objectives, target audience, and content — are clearly outlined before enrolment, and it is the responsibility of the delegate to ensure the course's suitability prior to booking.
For any inquiries related to cancellations or bookings, please contact our support team, who will be happy to assist you.